ROOK —— 一个云原生的开源的存储编排工具,提供了多种存储解决方案。
为什么选择ROOK
以往为k8s环境设置大容量存储的时候,要不选择NFS,要不选择高可用的Ceph集群。如果选择自己搭建NFS或者Ceph集群,因为对这些系统不熟悉,会遇到大大小小不同的坑,消耗着你原本并不宽裕的休息时间。
现在,有了ROOK,只需轻松设置几个参数,就可以让你快速完成集群搭建。而且存储集群还自带故障恢复,监控等等自动化的功能,省心省时省力。虽然现在云厂商一般都提供了自己存储方案,但在家、在公司搭测试环境下,ROOK还是很不错的。
下面是选择的是ROOK的Ceph集群方案,原因是这个方案可以充分利用Ceph原来的功能 :
- 单个Pod使用的持久化块存储
- 提供S3接口的对象存储功能
- 跨多个Pod共享的CephFS
集群环境介绍
系统: Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.4.0-48-generic x86_64)
Kubernetes: v1.18.3
机器:
| ip/host | 备注 | 角色 |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.31.101 ub1 | 虚拟机 1C4G 300G (笔记本i3-8100 vmware esix虚拟的ub1~3) | Master |
| 192.168.31.134 ub2 | 虚拟机 1C4G 300G | Master |
| 192.168.31.148 ub3 | 虚拟机 1C4G 300G | Master |
| 192.168.31.186 ub4 | 4C8G 30G 2.75T+2.75T+3.65T+150G (两个二手3T绿盘,一个4T西数蓝盘,一个家里淘汰的盘;机器是星际蜗牛B款) | Node |
| 192.168.31.144 ub5 | 虚拟机 1C8G 100G (主力机器R5-3600+32G,用多余的内存虚拟出来的) | Node |
这里搭Ceph用的硬盘都是ub4额外挂的硬盘。
安装前置要求
- ROOK https://rook.io/docs/rook/v1.5/k8s-pre-reqs.html
- Ceph https://rook.io/docs/rook/v1.5/k8s-pre-reqs.html
一般Ubuntu和Centos系统都直接满足要求,这里就不详细展开了。
清空磁盘
如果用来搭建集群的硬盘不是新的,在上面存了数据或者已经初始化为某种文件系统,就需要先清空磁盘。不然你要部署Operator的时候就会需要像我一样的问题:
rook-ceph-crash-collector-keyring secret not created for crash reporter
检查磁盘是否为空可以通过查看对应的设备FSTYPE是否为空
lsblk -f
NAME FSTYPE LABEL UUID MOUNTPOINT
vda
└─vda1 LVM2_member eSO50t-GkUV-YKTH-WsGq-hNJY-eKNf-3i07IB
├─ubuntu--vg-root ext4 c2366f76-6e21-4f10-a8f3-6776212e2fe4 /
└─ubuntu--vg-swap_1 swap 9492a3dc-ad75-47cd-9596-678e8cf17ff9 [SWAP]
vdb
如果不为空,可以用以下的命令清空硬盘
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdd bs=512K count=1
fdisk -l /dev/sdd
Disk /dev/sdd: 149.5 GiB, 160041885696 bytes, 312581808 sectors
Disk model: WDC WD1600AAJS-0
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
正式安装
1. 安装ROOK的Ceph集群Operator
git clone --single-branch --branch v1.4.7 https://github.com/rook/rook.git
cd rook/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph
kubectl create -f common.yaml
kubectl create -f operator.yaml
# kubectl create -f cluster.yaml
正确安装后就可以在在rook-ceph的命名空间里面,各个节点的csi插件csi-cephfsplugin和rook-discover磁盘发现服务安装好。
注意镜像需要翻墙获取
2. 安装Ceph集群
安装前需要根据机器情况修改配置
diff --git a/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/cluster.yaml b/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/cluster.yaml
index b57b8892..efc1c336 100644
--- a/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/cluster.yaml
+++ b/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/cluster.yaml
# 因为只用了一台机器上的磁盘,所以这个监控服务只用部署一个就行了
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ spec:
continueUpgradeAfterChecksEvenIfNotHealthy: false
# set the amount of mons to be started
mon:
- count: 3
+ count: 1
allowMultiplePerNode: false
mgr:
modules:
# 这两个配置是使用全部的节点上的全部磁盘,一般不推荐这样设置,因为它也会把默认的系统盘识别到里面。
@@ -176,8 +176,8 @@ spec:
# osd: rook-ceph-osd-priority-class
# mgr: rook-ceph-mgr-priority-class
storage: # cluster level storage configuration and selection
- useAllNodes: true
- useAllDevices: true
+ useAllNodes: false
+ useAllDevices: false
#deviceFilter:
config:
# metadataDevice: "md0" # specify a non-rotational storage so ceph-volume will use it as block db device of bluestore.
# 下面就是指定了ub4的各个使用硬盘名字
@@ -187,7 +187,7 @@ spec:
# encryptedDevice: "true" # the default value for this option is "false"
# Individual nodes and their config can be specified as well, but 'useAllNodes' above must be set to false. Then, only the named
# nodes below will be used as storage resources. Each node's 'name' field should match their 'kubernetes.io/hostname' label.
-# nodes:
+ nodes:
# - name: "172.17.4.201"
# devices: # specific devices to use for storage can be specified for each node
# - name: "sdb"
@@ -199,6 +199,12 @@ spec:
# storeType: filestore
# - name: "172.17.4.301"
# deviceFilter: "^sd."
+ - name: "192.168.31.186"
+ devices:
+ - name: "sdb"
+ - name: "sdc"
+ - name: "sdd"
+ - name: "sde"
# The section for configuring management of daemon disruptions during upgrade or fencing.
disruptionManagement:
# If true, the operator will create and manage PodDisruptionBudgets for OSD, Mon, RGW, and MDS daemons. OSD PDBs are managed dynamically
kubectl create -f cluster.yaml
启动成功后就能看到对应的osd启动,每个硬盘对应一个osd,所以我这里是4个。
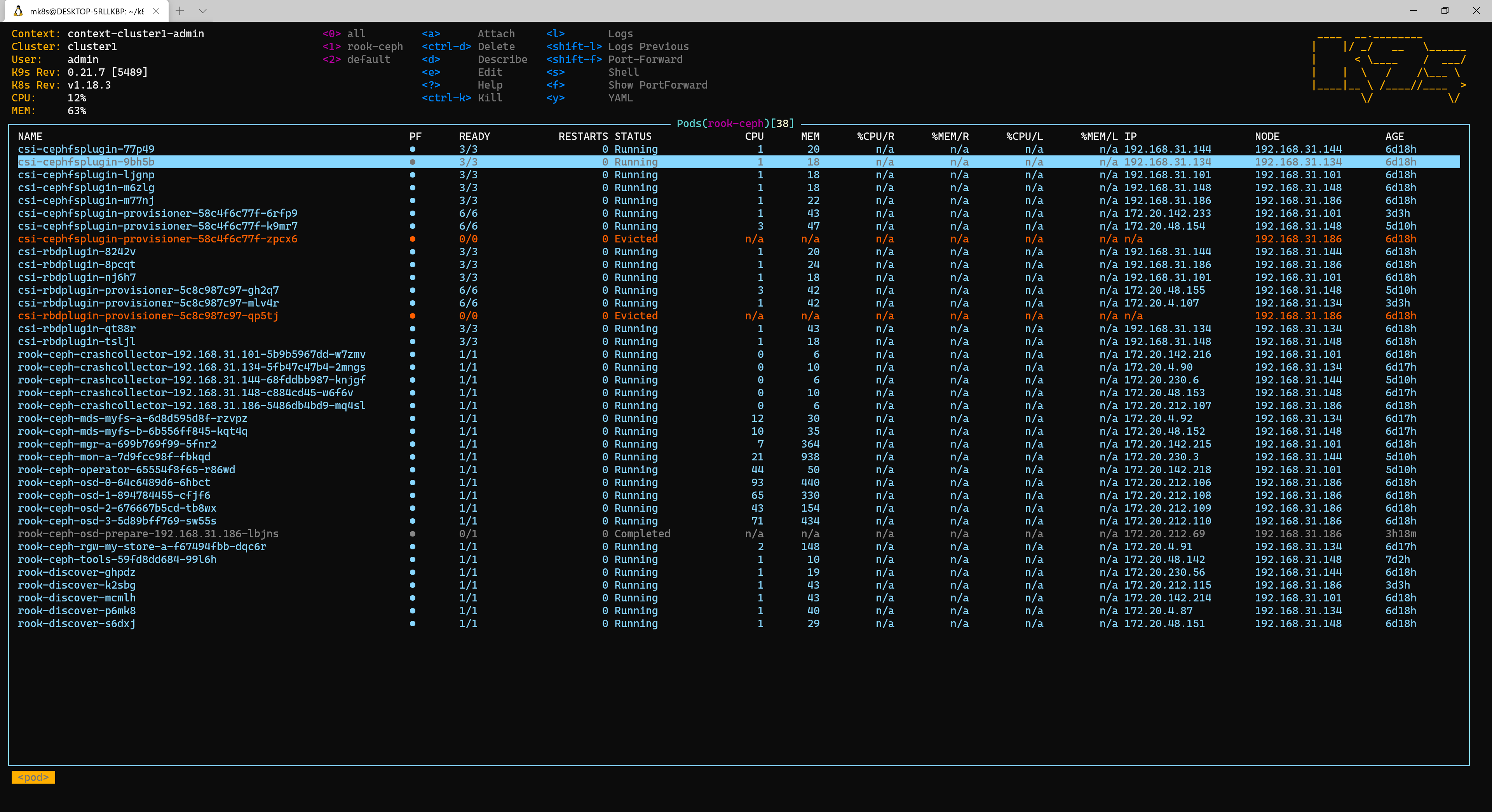
如何发现osd的数量不对,可以参考这个https://rook.io/docs/rook/v1.4/ceph-common-issues.html#osd-pods-are-not-created-on-my-devices看看是什么问题导致的。
3. 设置块存储StorageClass
原来故障恢复的主体是主机,所以需要至少3台主机。但因为我的硬盘都在一台机器上,这就要修改故障恢复的主体为osd。如果不需要做3副本,这里这可以设置为两副本。
diff --git a/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/object.yaml b/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/object.yaml
index dfadaee6..416e725c 100644
--- a/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/object.yaml
+++ b/cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/object.yaml
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ metadata:
spec:
# The pool spec used to create the metadata pools. Must use replication.
metadataPool:
- failureDomain: host
+ failureDomain: osd
replicated:
size: 3
# Disallow setting pool with replica 1, this could lead to data loss without recovery.
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ spec:
#target_size_ratio: ".5"
# The pool spec used to create the data pool. Can use replication or erasure coding.
dataPool:
- failureDomain: host
+ failureDomain: osd
replicated:
size: 3
# Disallow setting pool with replica 1, this could lead to data loss without recovery.
kubectl create -f object.yml
正常运行后就可以在StorageClass看到rook-ceph-block,这样部署应用的时候就可以方便持久化的存储了。
关于对象存储和CephFS的设置跟这里都大同小异,这里就不继续了。
4. 其他安装问题
如果有其他问题导致安装失败,可以看官网提供的ceph常见问题文档
5. 常用工具
默认安装的Operator包含了Dashboard,不过没有设置访问方式。需要自己添加Service暴露服务.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rook-ceph-mgr-dashboard-external-https
namespace: rook-ceph
labels:
app: rook-ceph-mgr
rook_cluster: rook-ceph
spec:
ports:
- name: dashboard
port: 8443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8443
selector:
app: rook-ceph-mgr
rook_cluster: rook-ceph
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
kubectl create -f dashboard-external-https.yaml
$ kubectl -n rook-ceph get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
rook-ceph-mgr ClusterIP 10.108.111.192 <none> 9283/TCP 4h
rook-ceph-mgr-dashboard ClusterIP 10.110.113.240 <none> 8443/TCP 4h
rook-ceph-mgr-dashboard-external-https NodePort 10.101.209.6 <none> 8443:31176/TCP 4h
默认的安装包含了一个admin的账户,获取密码的方式如下
kubectl -n rook-ceph get secret rook-ceph-dashboard-password -o jsonpath="{['data']['password']}" | base64 --decode && echo
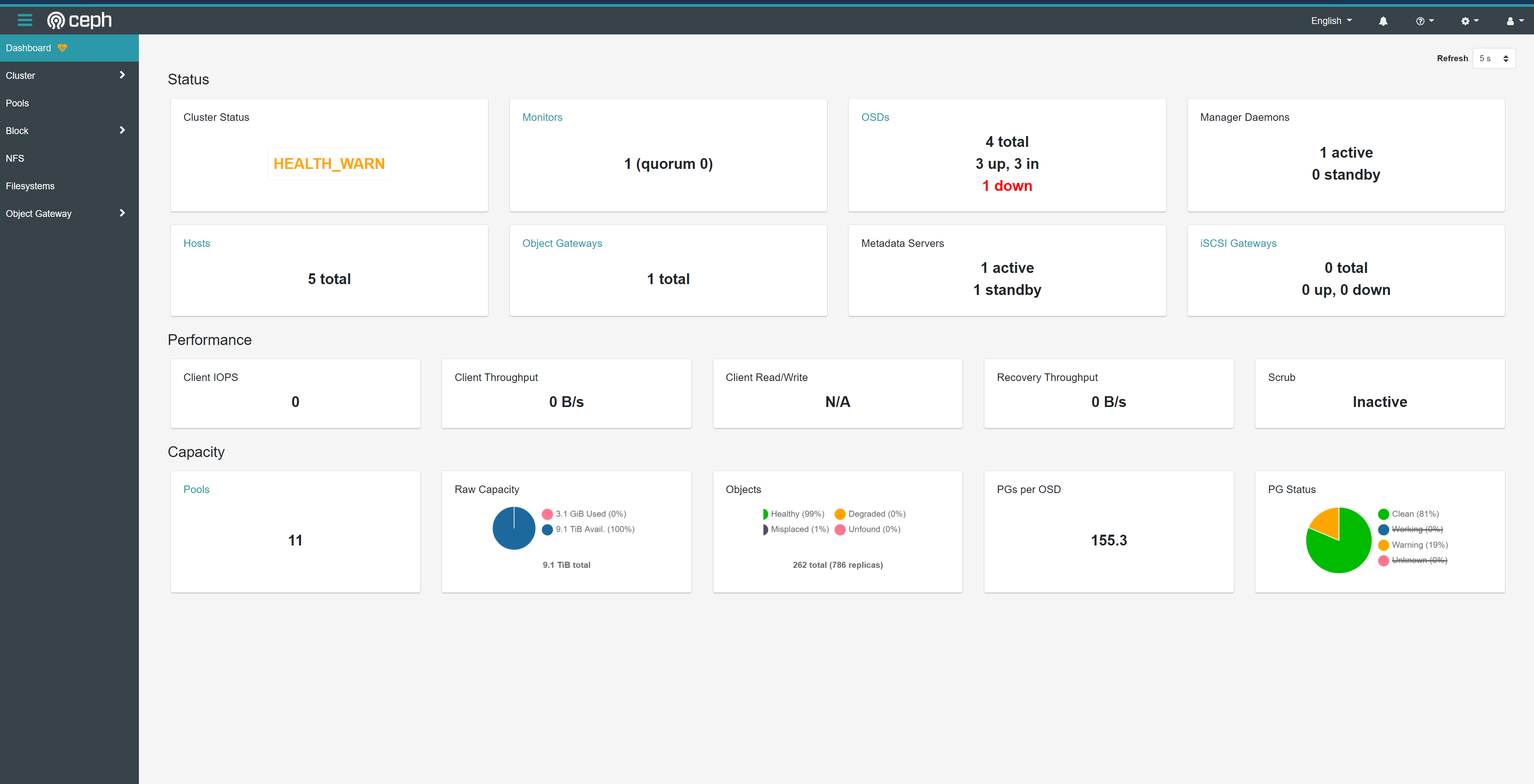
现在访问任意节点的 31176端口就可以看到下面的界面